YOLO - object detection¶
YOLO — You Only Look Once — is an extremely fast multi object detection algorithm which uses convolutional neural network (CNN) to detect and identify objects.
The neural network has this network architecture.
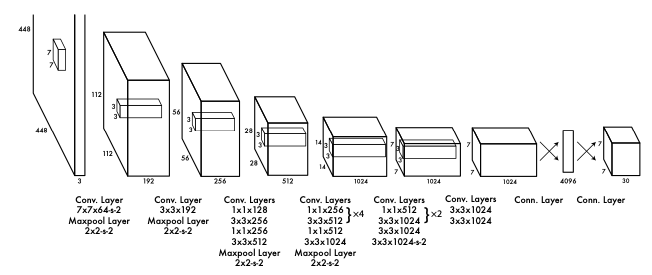
Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.02640.pdf
This is our input image:

Load the YOLO network¶
In order to run the network you will have to download the pre-trained YOLO weight file (237 MB). https://pjreddie.com/media/files/yolov3.weights
Also download the the YOLO configuration file.
You can now load the YOLO network model from the harddisk into OpenCV:
net = cv.dnn.readNetFromDarknet('yolov3.cfg', 'yolov3.weights')
net.setPreferableBackend(cv.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
The YOLO neural network has 254 components. You can print them to the console with:
ln = net.getLayerNames()
print(len(ln), ln)
The 524 elements consist of convolutional layers (conv),
rectifier linear units (relu) etc.:
254 ['conv_0', 'bn_0', 'relu_0', 'conv_1', 'bn_1', 'relu_1', 'conv_2', 'bn_2',
'relu_2', 'conv_3', 'bn_3', 'relu_3', 'shortcut_4', 'conv_5', 'bn_5', 'relu_5',
'conv_6', 'bn_6', 'relu_6', 'conv_7', 'bn_7', 'relu_7', 'shortcut_8', 'conv_9',
'bn_9', 'relu_9', 'conv_10', 'bn_10', 'relu_10', 'shortcut_11', 'conv_12', 'bn_12',
...
Create a blob¶
The input to the network is a so-called blob object.
The function cv.dnn.blobFromImage(img, scale, size, mean) transforms the image into a blob:
blob = cv.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1/255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False)
It has the following parameters:
- the image to transform
- the scale factor (1/255 to scale the pixel values to [0..1])
- the size, here a 416x416 square image
- the mean value (default=0)
- the option swapBR=True (since OpenCV uses BGR)
A blob is a 4D numpy array object (images, channels, width, height). The image below shows the red channel of the blob. You notice the brightness of the red jacket in the background.
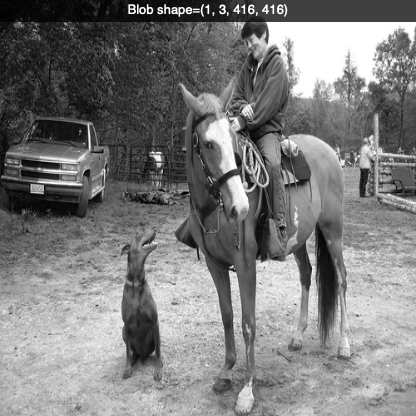

# YOLO object detection
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import time
img = cv.imread('images/horse.jpg')
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.waitKey(1)
# Give the configuration and weight files for the model and load the network.
net = cv.dnn.readNetFromDarknet('yolov3.cfg', 'yolov3.weights')
net.setPreferableBackend(cv.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
# net.setPreferableTarget(cv.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
ln = net.getLayerNames()
print(len(ln), ln)
# construct a blob from the image
blob = cv.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1/255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False)
r = blob[0, 0, :, :]
cv.imshow('blob', r)
text = f'Blob shape={blob.shape}'
cv.displayOverlay('blob', text)
cv.waitKey(1)
net.setInput(blob)
t0 = time.time()
outputs = net.forward(ln)
t = time.time()
cv.displayOverlay('window', f'forward propagation time={t-t0}')
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
The blob object is given as input to the network:
net.setInput(blob)
t0 = time.time()
outputs = net.forward(ln)
t = time.time()
The forward propagation takes about 2 seconds on an MacAir 2012 (1,7 GHz Intel Core i5).
And the 80 COCO class names.
Identifiy objects¶
These two instructions calculate the network response:
net.setInput(blob)
outputs = net.forward(ln)
The outputs object are vectors of lenght 85
- 4x the bounding box (centerx, centery, width, height)
- 1x box confidence
- 80x class confidence
We add a slider to select the BoundingBox confidence level from 0 to 1.

The final image is this:
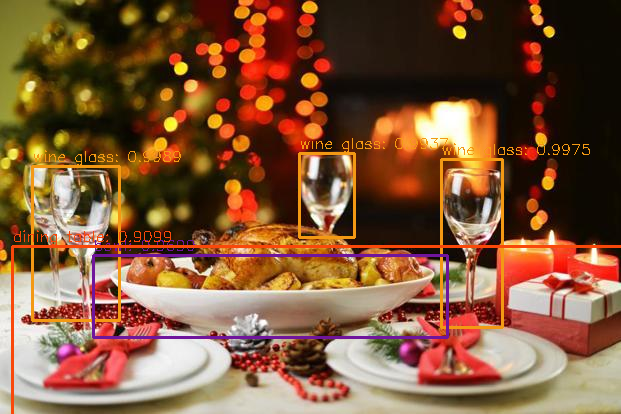

# YOLO object detection
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import time
img = cv.imread('images/food.jpg')
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.waitKey(1)
# Load names of classes and get random colors
classes = open('coco.names').read().strip().split('\n')
np.random.seed(42)
colors = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(classes), 3), dtype='uint8')
# Give the configuration and weight files for the model and load the network.
net = cv.dnn.readNetFromDarknet('yolov3.cfg', 'yolov3.weights')
net.setPreferableBackend(cv.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
# net.setPreferableTarget(cv.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
# determine the output layer
ln = net.getLayerNames()
ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# construct a blob from the image
blob = cv.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1/255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False)
r = blob[0, 0, :, :]
cv.imshow('blob', r)
text = f'Blob shape={blob.shape}'
cv.displayOverlay('blob', text)
cv.waitKey(1)
net.setInput(blob)
t0 = time.time()
outputs = net.forward(ln)
t = time.time()
print('time=', t-t0)
print(len(outputs))
for out in outputs:
print(out.shape)
def trackbar2(x):
confidence = x/100
r = r0.copy()
for output in np.vstack(outputs):
if output[4] > confidence:
x, y, w, h = output[:4]
p0 = int((x-w/2)*416), int((y-h/2)*416)
p1 = int((x+w/2)*416), int((y+h/2)*416)
cv.rectangle(r, p0, p1, 1, 1)
cv.imshow('blob', r)
text = f'Bbox confidence={confidence}'
cv.displayOverlay('blob', text)
r0 = blob[0, 0, :, :]
r = r0.copy()
cv.imshow('blob', r)
cv.createTrackbar('confidence', 'blob', 50, 101, trackbar2)
trackbar2(50)
boxes = []
confidences = []
classIDs = []
h, w = img.shape[:2]
for output in outputs:
for detection in output:
scores = detection[5:]
classID = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classID]
if confidence > 0.5:
box = detection[:4] * np.array([w, h, w, h])
(centerX, centerY, width, height) = box.astype("int")
x = int(centerX - (width / 2))
y = int(centerY - (height / 2))
box = [x, y, int(width), int(height)]
boxes.append(box)
confidences.append(float(confidence))
classIDs.append(classID)
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, 0.5, 0.4)
if len(indices) > 0:
for i in indices.flatten():
(x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1])
(w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3])
color = [int(c) for c in colors[classIDs[i]]]
cv.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(classes[classIDs[i]], confidences[i])
cv.putText(img, text, (x, y - 5), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 1)
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.waitKey(0)
cv.destroyAllWindows()
3 Scales for handling different sizes¶
The YOLO network has 3 outputs:
- 507 (13 x 13 x 3) for large objects
- 2028 (26 x 26 x 3) for medium objects
- 8112 (52 x 52 x 3) for small objects
Detecting objects¶
In this program example we are going to detect objects in multiple imgages.
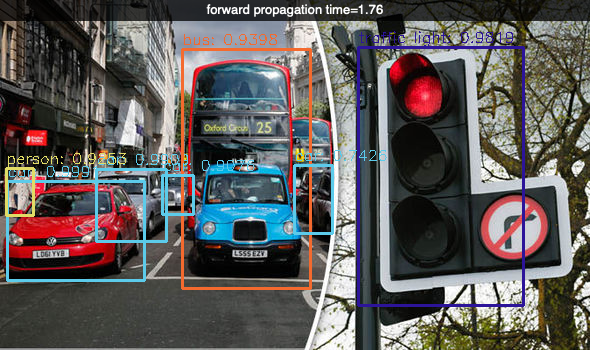
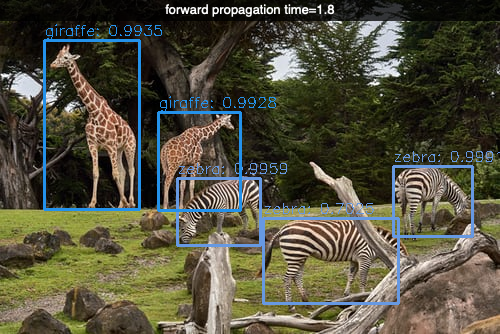
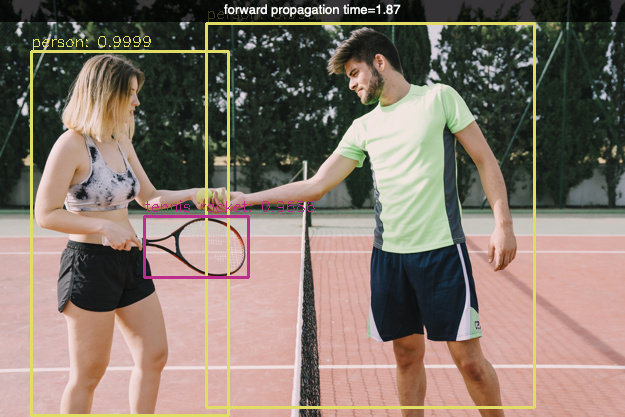
# YOLO object detection
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
import time
WHITE = (255, 255, 255)
img = None
img0 = None
outputs = None
# Load names of classes and get random colors
classes = open('coco.names').read().strip().split('\n')
np.random.seed(42)
colors = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(len(classes), 3), dtype='uint8')
# Give the configuration and weight files for the model and load the network.
net = cv.dnn.readNetFromDarknet('yolov3.cfg', 'yolov3.weights')
net.setPreferableBackend(cv.dnn.DNN_BACKEND_OPENCV)
# net.setPreferableTarget(cv.dnn.DNN_TARGET_CPU)
# determine the output layer
ln = net.getLayerNames()
ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
def load_image(path):
global img, img0, outputs, ln
img0 = cv.imread(path)
img = img0.copy()
blob = cv.dnn.blobFromImage(img, 1/255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
t0 = time.time()
outputs = net.forward(ln)
t = time.time() - t0
# combine the 3 output groups into 1 (10647, 85)
# large objects (507, 85)
# medium objects (2028, 85)
# small objects (8112, 85)
outputs = np.vstack(outputs)
post_process(img, outputs, 0.5)
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.displayOverlay('window', f'forward propagation time={t:.3}')
cv.waitKey(0)
def post_process(img, outputs, conf):
H, W = img.shape[:2]
boxes = []
confidences = []
classIDs = []
for output in outputs:
scores = output[5:]
classID = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classID]
if confidence > conf:
x, y, w, h = output[:4] * np.array([W, H, W, H])
p0 = int(x - w//2), int(y - h//2)
p1 = int(x + w//2), int(y + h//2)
boxes.append([*p0, int(w), int(h)])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
classIDs.append(classID)
# cv.rectangle(img, p0, p1, WHITE, 1)
indices = cv.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, conf, conf-0.1)
if len(indices) > 0:
for i in indices.flatten():
(x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1])
(w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3])
color = [int(c) for c in colors[classIDs[i]]]
cv.rectangle(img, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), color, 2)
text = "{}: {:.4f}".format(classes[classIDs[i]], confidences[i])
cv.putText(img, text, (x, y - 5), cv.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, color, 1)
def trackbar(x):
global img
conf = x/100
img = img0.copy()
post_process(img, outputs, conf)
cv.displayOverlay('window', f'confidence level={conf}')
cv.imshow('window', img)
cv.namedWindow('window')
cv.createTrackbar('confidence', 'window', 50, 100, trackbar)
load_image('images/horse.jpg')
load_image('images/traffic.jpg')
load_image('images/zoo.jpg')
load_image('images/kitchen.jpg')
load_image('images/airport.jpg')
load_image('images/tennis.jpg')
load_image('images/wine.jpg')
load_image('images/bicycle.jpg')
cv.destroyAllWindows()